In Switzerland, many people choose car leasing instead of buying a car. The monthly payments seem attractive, and access to new models is easy.
However, among leasing enthusiasts, interest in car subscription models is also growing. These offer the same advantages as car leasing, but additionally convince with simpler handling, lower costs, and complete cost transparency, as services such as insurance and tyres are already included in the monthly fixed price.
In this article, you will learn how car leasing works in Switzerland, what advantages and disadvantages it has, and why a car subscription has become a popular alternative for many leasing customers. We also show the most important terms, cost traps, and pitfalls.
INFOBOX
The car subscription from Carvolution is the simple, flexible, and cost-effective alternative to buying a car – and leasing. With a car subscription, you simply choose your car on Carvolution.ch, select the term between 3 and 48 months, and choose a monthly mileage package between 350 km and 3,250 km – which can be adjusted flexibly. The subscription comes at a monthly fixed price, which already includes all additional costs around the car: comprehensive insurance, registration, taxes, service and maintenance, tyres, initial motorway vignette, and a fuel card.
Car Leasing in Switzerland
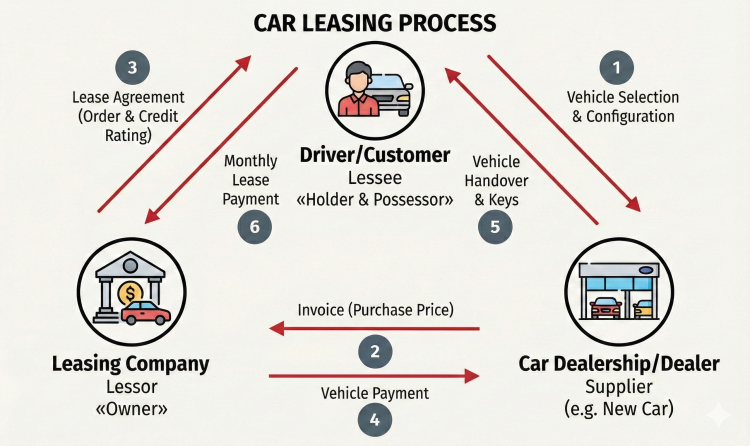
Car leasing is a form of financing in which a leasing company purchases an asset – in this case a car – and allows the lessee (you) to use it for a fixed period in exchange for monthly leasing payments.
How common is car leasing in Switzerland?
In Switzerland, car leasing has long been established as a common form of financing: every second car is financed externally, most of them through leasing. Approximately one in three cars on the country’s roads is leased. This share has remained relatively stable for several years. At the same time, interest in new mobility models such as car subscriptions is growing, as classic leasing contracts with fixed terms and mileage limits often no longer suit modern lifestyles.
Among these leased cars are not only private cars, but also numerous company cars. Corporate leasing differs significantly from private leasing, particularly regarding taxation. Private individuals do not benefit from tax advantages when leasing, while companies can.
Note: From here, this article focuses on private leasing.
Why do many people choose car leasing?
The main reason for the popularity of leasing lies in the comparatively low monthly payments. Instead of investing a large sum at once, you can drive a car and spread the costs over several years.
Besides the financial advantage, lifestyle also plays a major role: leasing allows you to drive new cars regularly and benefit from the latest technology and advanced safety features.
Furthermore, with leasing, the residual value risk is eliminated, as the car can simply be returned at the end of the contract. This is particularly advantageous for electric cars, because due to intense competition and a fast innovation cycle (e.g., new 800-volt architectures), older electric car models lose value much faster than comparable combustion cars. For car buyers, this represents a noticeable financial risk, which is eliminated with both leasing and car subscriptions.
Nevertheless, caution is advised: the low monthly payments in leasing do not reflect the full costs of the car. Insurance, maintenance, tyres, taxes, and more can significantly increase the actual financial burden – as Stephan’s experience also shows. Therefore, before you start, you should realistically calculate what your leasing actually costs.
With a car subscription, these costs are already included: insurance, maintenance, and tyres are part of the monthly price, giving you full cost control and no unpleasant surprises.
Who is car leasing suitable for – and who is not?
Leasing is ideal for drivers who want to use a new, precisely configured car over 3–4 years. With a car subscription, you can also drive a new car – although not self-configured, but still well-equipped and overall cheaper than leasing.
Those who require flexibility, for example due to a sudden move back to their home country, quickly reach the limits of leasing, as rigid contracts make early termination difficult. For expats in Switzerland seeking uncomplicated mobility, leasing may therefore be the wrong choice.
Retirees also face challenges: leasing as a retiree often fails due to insufficient or irregular income.
In such cases, a car subscription provides the perfect bridge for expats and retirees – cheaper, more flexible, and available to everyone.
Basic Knowledge: What Does Car Leasing Mean?
Before signing a contract, you should know exactly what you are committing to.
Car Leasing Simply Explained
With car leasing, you do not buy the car, but use it over a longer period in exchange for a monthly payment. You are the registered keeper of the car, but the leasing company remains the owner.
This means you must take good care of the car, as excessive wear or damage can be charged at the end. Before signing, it is worth reviewing the five most important questions about leasing to have all key points in view.
Special considerations apply to electric cars in leasing. Here you can find all essential information at a glance.
Purchase vs. Financing vs. Car Leasing vs. Car Subscription
The decision to get a new car mainly depends on how much capital you want to tie up and how important ownership of the car is.
With outright purchase, the car belongs to you immediately. You make a large one-time payment, which strongly limits your liquidity. No interest is charged, but you bear the full risk of depreciation.
With credit financing, the car also belongs to you immediately. Instead of a large one-time payment, you can spread the costs over monthly installments and interest, making the burden easier to plan. You still bear the full risk of depreciation. For a better understanding, it is worth looking at the leasing vs. financing comparison.
With car leasing, the car does not belong to you; you use it over a longer period for a monthly rate. You are the keeper, and the leasing company remains the owner. To assess the actual monthly burden correctly, you should calculate leasing costs carefully in advance.
Important: In all options mentioned, only financing and interest are included. Additional costs such as comprehensive insurance, registration, taxes, service and maintenance, and tyres are extra.
Since these options are not ideal solutions for everyone, car subscriptions are becoming increasingly popular. Like leasing, you do not own the car and do not bear residual value risk. You have monthly costs, similar to leasing or credit financing – but all the expenses mentioned above are already included and managed through a single provider. Another big advantage is flexible terms and adjustable monthly mileage.
Why Kilian Found Choosing Between Leasing and a Car Subscription Difficult – and Why He Ultimately Chose the Car Subscription
You can read our interview to see why he chose the subscription – and more customer experiences are available here.
In our comprehensive comparison of purchase, leasing, or car subscription, we also show the financial effects of the different models in detail. If you have not yet decided on a car model, our guide Which Car Suits You? will help.
The Most Important Car Leasing Terms
To lease a car cheaply, you need to understand the language of sellers:
Leasing Interest (Effective Annual Rate)
The interest is the fee for the capital provided by the leasing company. The effective annual rate is crucial, as it includes all costs and fees and is therefore the only reliable basis for price comparison. Beware of 0% leasing: as dealers earn nothing on the financing, discounts on the car price are often removed, or compulsory service packages are added.
Residual Value
This is the estimated market value of the car at the end of the lease – it is the biggest lever for your monthly payment. At the end of the lease, you usually have the choice to buy the car or not. Note the following:
Buying: Try to negotiate a low residual value with the leasing company, so you pay less if you purchase. Check if there is a purchase option; otherwise, the dealer can sell the car at a higher market price.
Not buying: Aim for a higher residual value to keep your monthly payments low.
Down Payment (Initial Large Payment)
A down payment reduces the financed sum from the start. Leasing without a down payment conserves your savings but leads to higher monthly payments and higher total interest.
Mileage Limit
Leasing sets a total mileage for the contract period, usually 2–4 years. Typically, annual mileage ranges from 5,000 to 20,000+ km, depending on the contract. Excess mileage is charged extra per kilometre, often several cents per km depending on the car model. These extra costs can significantly increase monthly expenses.
The agreed mileage usually cannot be adjusted later, so it’s important to realistically estimate your usage to avoid additional payments. If you often exceed the mileage, consider these costs in your planning or check alternatives like a car subscription.
With a car subscription, you select a mileage package at the start and can adjust it monthly via the app.
Comprehensive Insurance & GAP Coverage
Since the car belongs to the leasing company, comprehensive insurance is mandatory in Switzerland. With purchase or financing, partial insurance is also possible, while liability insurance is mandatory in all cases.
A critical issue is total loss: insurance often pays only the current market value, usually below the remaining lease balance. A GAP insurance (Guaranteed Asset Protection) covers this difference.
With a car subscription, comprehensive insurance and optional parking and legal protection coverage are included – for worry-free driving.
The Actual Costs: What Does Car Leasing Really Cost?
Many Swiss people calculate only the monthly lease payment for car leasing. This is the biggest mistake, as the leasing rate only shows part of the truth.
Costs Included in the Lease Payment
The monthly lease payment forms the core of every leasing calculation in Switzerland. It consists of two main components:
Depreciation: You pay the difference between the purchase price and the calculated residual value at the end of the term. This amount is spread evenly over the months.
Interest: The leasing interest is the fee the leasing company charges for the capital provided. It is based on the effective annual rate and represents the financing portion of the payment.
Costs That Arise Separately (Additional Costs)
Here lie the biggest budget traps. These costs must be paid separately and organised by the lessee:
Insurance: In Switzerland, comprehensive insurance is mandatory for leased cars. Depending on the car, the price usually ranges from CHF 80–180+ per month. GAP coverage is strongly recommended but often not included.
Tyres: Costs for winter tyres, biannual tyre changes, and storage typically amount to CHF 20–50 per month.
Service & Maintenance: All required service intervals must be observed, and the lessee bears the full cost. Depending on the car, this can be CHF 40–100+ per month.
Taxes & Fees: In addition to cantonal road taxes, registration fees, and administrative charges apply, usually CHF 15–50 per month.
Return Costs: The Unpleasant Surprise at the End
At the end of the term, the car is inspected. Additional costs often arise due to:
Damage: Scratches, dents, or interior wear beyond “normal use” are charged.
Excess Mileage: If you exceed the agreed mileage, additional charges per km apply.
Other Fees: Failure to comply with contract terms may result in extra charges, e.g., missing documents or skipped services.
Risks of Early Termination
A leasing contract is legally very rigid. Early termination – for example due to a job change or moving abroad – can be extremely expensive.
Firstly, a prepayment penalty may apply.
Secondly, a retroactive recalculation of payments occurs: since the car is now depreciated over a shorter period, the leasing company demands the difference to the much higher short-term lease rate for the elapsed period.
A lease transfer to a third party can be a suitable, though often cumbersome, alternative to avoid these costs.
The Simple Rule of Thumb
To realistically calculate leasing costs, all expenses must be considered – not just the monthly payment. If you don’t have time to calculate everything in detail, this simple rule helps:
Lease Payment × 3 ≈ Actual Monthly Total Costs
This way, you can quickly estimate how much a leased car really costs.
This is exactly where Carvolution’s car subscription comes in: with our best price guarantee, Carvolution ensures that the Carvolution all-inclusive subscription is cheaper than the total monthly costs of a comparable lease.
Comparing Car Leasing Costs
An offer with low monthly payments is tempting – but not automatically cheap. To really compare leasing, you should consider all costs carefully. In our interview with Sascha, you can see why he ultimately switched to a car subscription after a leasing comparison.
Important Comparison Parameters: Your Checklist
To fairly compare two leasing offers, the conditions must be identical. Use this checklist:
Lease Payment: Make sure the effective annual rate is stated. Only then can you see the real financing cost. Many providers advertise low nominal rates to appear attractive without making costs transparent.
Residual Value: Compare the calculated residual value carefully. If you do not want to buy the car, a higher residual value can be sensible, as it lowers monthly payments. If you plan to buy, aim for a lower residual value. Check for a purchase option; otherwise, the dealer may sell the car at a higher market price.
Term: Longer contracts (e.g., 48 months) reduce the monthly payment but bind you longer. Shorter contracts are more flexible, with higher monthly payments. Choose the term that fits your life.
Mileage Limit: Compare only offers with the same mileage. Even 5,000 km difference per year can distort costs. If you exceed the agreed mileage, extra charges per km apply.
Using Online Leasing Calculators Correctly
An online leasing calculator is a useful tool but only as accurate as your inputs. Be completely honest with yourself.
Realistic Mileage: If you think you will drive 15,000 km, calculate with 15,000 km – not 10,000 km just to make the monthly payment look lower. Otherwise, the final bill will be more expensive.
Realistic Term: Choose the term you can actually maintain. Early termination ruins the calculation.
Typical Provider Tricks
Providers often use psychological tricks to make leasing offers appear cheaper. Watch out for:
Promotional Interest Rates: Extremely low rates (e.g., 0.9 %) usually only apply to stock cars or very short terms. If you configure your car individually, the rate usually rises significantly.
Compulsory Options: Some special offers tie you to expensive additional insurance or maintenance packages that could be cheaper elsewhere.
Down Payment Trick: High down payments lower the advertised monthly payment, but total costs over the term remain high. Always check the total amount, not just the rate.
If you have to consider all these points in leasing, you can quickly lose track – with a car subscription, this does not happen. You pay a monthly fixed price in which almost all costs are included, and there are no unpleasant surprises.
Requirements for Car Leasing
Before leasing a car, the leasing company checks legal requirements, conducts a credit check, and evaluates financial feasibility.
Legal Requirements
To conclude a valid leasing contract, the following conditions must be met:
Age: You must be at least 18 years old.
Residence: A permanent residence in Switzerland or Liechtenstein is required.
Residence Permit (for foreign nationals): Usually, a B or C permit is required. Its validity should ideally cover the planned lease term.
Credit Check
Leasing companies check your financial reliability to minimise default risk:
ZEK Report: The Central Office for Credit Information (ZEK) records ongoing loans, leasing contracts, and payment behaviour. Negative entries like late payments or terminated contracts often lead to rejection.
Debt Collection Extract: Open debts, seizures, or loss certificates are a clear exclusion. Completed entries are evaluated differently by each bank and do not automatically lead to rejection.
Financial Feasibility
The leasing company verifies that you can afford the lease payments long-term without jeopardising your subsistence minimum:
Stable Income: Regular income from a permanent position is preferred. Self-employed people usually provide balance sheets or tax documents for the last two to three years.
Legal Feasibility Check: According to the Swiss Consumer Credit Act, the leasing company must ensure that the lease payments do not exceed your financial capacity.
Orientation Value 30%: As a guideline, monthly obligations (lease payments plus other ongoing payments) should not exceed about 30% of disposable income. This can vary depending on the bank and individual situation.
If you want to learn more about requirements, read our detailed blog: Leasing Requirements: How It Works in Switzerland!
Advantages and Disadvantages of Leasing at a Glance
Car Subscription as a Flexible Alternative
If leasing is too complicated or rigid, or you just don’t want paperwork, there is a modern solution: the car subscription. Read here how a car subscription works.
What is a Car Subscription?
A car subscription from Carvolution is a true all-in-one package. In a single fixed monthly payment, everything that normally costs extra is included:
Insurance
Service & Maintenance
Tyre Changes
Taxes
Cantonal Registration
Maximum Flexibility: While classic leasing often binds you for 36 or 48 months, with a car subscription, you can start from 3 months and stay up to 48 months – whatever suits you. Your mileage package can be adjusted monthly via the app if you drive more or less. This avoids excess mileage costs. And if you fall in love with the car, you can simply buy it at the end of the subscription.
Differences to Classic Car Leasing
True Cost Transparency: With leasing, you usually only pay the “rent” for the car – additional costs for insurance, service, tyres, or taxes often come on top. With a car subscription, all relevant costs around the car are included in the monthly payment, and you don’t have to worry about anything: the car is registered, insured, taxed, tyres stored, and much more. The best part: if you include all extra costs, a car subscription is even cheaper than comparable leasing. We guarantee this with our best price guarantee.
Everything from One Source: One contract, everything managed – no annoying insurance comparisons, no hunting for workshops. Saves time, money, and nerves.
Flexibility: As mentioned, the subscription offers terms from 3 to 48 months and adjustable mileage, so you can adapt the subscription to your life situation at any time.
Curious? Book a consultation now – we answer all questions and help make your mobility simpler, more flexible, and most importantly, cost-effective.
Get the Supersavers
Discover new special offer models at unbeatable prices, such as the Opel Corsa from CHF 259.–. More top deals on Fiat, BMW & Peugeot models.










